byteDEVKIT-am62x (Yocto 4.0)
Downloads
SD card image
Download |
Checksum (SHA256) |
|---|---|
0747dfb463edad01cd3bf7985bed602e717b1dfa2f09258ed6860c37b57c67cb |
|
3577b6bc71600903fcba120629a50f5595e25f9ceb63d6301efb3f46d3848115 |
Hint
Updating from an older image?
You can update your older image by using: apt-get update and apt-get upgrade.
check for new version in the table above
edit
/etc/apt/sources.listand point to the new package feedrun
apt-get update; apt-get upgrade
As the yocto framework is based on several packages from various projects or suppliers, it is not guaranteed that
an incremental upgrade by apt-get upgrade works automatically. Some manual adjustments might be needed.
Toolchain
Download |
Checksum (SHA256) |
|---|---|
poky-bytesatwork-glibc-x86_64-bytesatwork-minimal-image-aarch64-bytedevkit-am62x-toolchain-4.0.9.sh |
a5e9e6706cbff94fb3e31b41e948cbe1665cabca457e1bf337c59d45d6616c82 |
U-Boot
Description |
Download |
Checksum (SHA256) |
|---|---|---|
SPL R5F |
53481b110634d711c43c47db40b2cfbce8b993cc6b63892d204d6563f35ea690 |
|
SPL A53 |
ee581879fba5a58dc872395eda734e5fe4d5bfdc4a4eb48b7e09b21991827908 |
|
U-Boot A53 |
7c14d88c61772c3bb36d4d1441eee46f3d64f4d5d5abbb1b0ba2a264247a20aa |
Image
How do you flash the image?
Attention
You need a microSD card with at least 8GB capacity.
All existing data on the microSD card will be lost.
Do not format the microSD card before flashing.
Windows
Unzip the file
bytesatwork-minimal-image-bytedevkit-am62x.wic.gz(e.g. with 7-zip)Write the resulting file to the microSD card with a tool like Roadkils Disk Image
Linux
gunzip -c bytesatwork-minimal-image-bytedevkit-am62x.wic.gz | dd of=/dev/mmcblk<X> bs=8M conv=fsync status=progress
Hint
To improve write performance, you could use bmap-tools under Linux:
bmaptool copy bytesatwork-minimal-image-bytedevkit-am62x.wic.gz /dev/mmcblk<X>
How do you build an image?
Use repo to download all necessary repositories:
$ mkdir -p ~/workdir/bytedevkit-am62x/4.0; cd ~/workdir/bytedevkit-am62x/4.0
$ repo init -b kirkstone -u https://github.com/bytesatwork/bsp-platform-ti.git
$ repo sync
If those commands are completed successfully, the following command will set up a Yocto Project environment for byteDEVKIT-am62x:
$ cd ~/workdir/bytedevkit-am62x/4.0
$ MACHINE=bytedevkit-am62x DISTRO=poky-bytesatwork EULA=1 . setup-environment build
The final command builds the development image:
$ cd $BUILDDIR
$ bitbake bytesatwork-minimal-image
The output is found in:
~/workdir/bytedevkit-am62x/4.0/build/tmp/deploy/images/bytedevkit-am62x
Hint
For additional information about yocto images and how to build them, please visit: https://docs.yoctoproject.org/4.0.9/brief-yoctoprojectqs/index.html#building-your-image.
How to modify the image
The image recipes can be found in
~/workdir/bytedevkit-am62x/4.0/sources/meta-bytesatwork/recipes-core/imagesThis is relative to where you started the
repocommand to fetch all the sources.Edit the minimal-image recipe
bytesatwork-minimal-image.bbAdd the desired software-package to
IMAGE_INSTALLvariable, for example addnet-toolstobytesatwork-minimal-image.bbRebuild the image by:
$ cd ~/workdir/bytedevkit-am62x/4.0 $ MACHINE=bytedevkit-am62x DISTRO=poky-bytesatwork EULA=1 . setup-environment build $ bitbake bytesatwork-minimal-image
How to rename the image
If you want to rename or copy an image, simply rename or copy the image recipe by:
$ cd ~/workdir/bytedevkit-am62x/4.0/sources/meta-bytesatwork/recipes-core/images $ cp bytesatwork-minimal-image.bb customer-example-image.bb
Troubleshooting
Image size is too small
If you encounter that your image size is too small to install additional software, please have a look at the
IMAGE_ROOTFS_SIZEvariable under~/workdir/bytedevkit-am62x/4.0/sources/meta-bytesatwork/recipes-core/images/bytesatwork-minimal-image.bb. Increase the size if necessary.
Toolchain
How do you install the toolchain?
Simply download the toolchain and execute the downloaded file, which is a self-extracting shell script.
Hint
If you encounter problems when trying to install the toolchain, make sure the downloaded toolchain is executable. Run chmod +x /<path>/<toolchain-file>.sh to make it executable.
Important
- The following tools need to be installed on your development system:
xz(Debian package:xz-utils)python(any version)gcc
How do you use the toolchain?
Source the installed toolchain:
source /opt/poky-bytesatwork/4.0.9/environment-setup-aarch64-poky-linux
Check if Cross-compiler is available in environment:
echo $CC
You should see the following output:
aarch64-poky-linux-gcc -fstack-protector-strong -O2 -D_FORTIFY_SOURCE=2 -Wformat -Wformat-security -Werror=format-security --sysroot=/opt/poky-bytesatwork/4.0.9_bytedevkit-am62x/sysroots/aarch64-poky-linux
Crosscompile the source code, e.g. by:
$CC helloworld.c -o helloworld
Check generated binary:
file helloworld
The output that is shown in prompt afterwards:
helloworld: ELF 64-bit LSB pie executable, ARM aarch64, version 1 (SYSV), dynamically linked, interpreter /lib/ld-linux-aarch64.so.1, BuildID[sha1]=257792938c3ed4fbf6b15d071c60973ab51b2f37, for GNU/Linux 3.14.0, with debug_info, not stripped
How to bring your binary to the target?
Connect the embedded device’s ethernet to your LAN
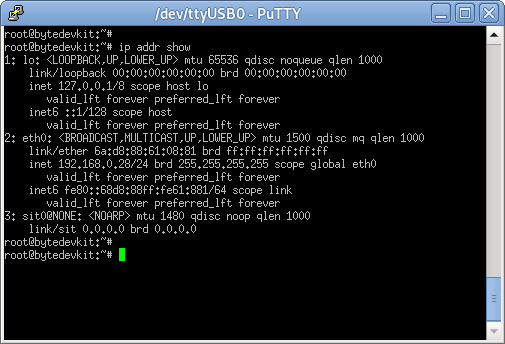
Determine the embedded target IP address by
ip addr show
Copy your binary, e.g.
helloworldto the target byscp helloworld root@<ip address of target>:/tmp

Run
chmod +xon the target to make your binary executable:chmod +x /<path>/<binary name>Run your binary on the target:
/<path>/<binary name>
How do you build a toolchain?
$ cd ~/workdir/bytedevkit-am62x/4.0
$ repo init -b kirkstone -u https://github.com/bytesatwork/bsp-platform-ti.git
$ repo sync
If those commands are completed successfully, the following command will set up a Yocto Project environment for byteDEVKIT-am62x:
$ cd ~/workdir/bytedevkit-am62x/4.0
$ MACHINE=bytedevkit-am62x DISTRO=poky-bytesatwork EULA=1 . setup-environment build
The final command builds an installable toolchain:
$ cd $BUILDDIR
$ bitbake bytesatwork-minimal-image -c populate_sdk
The toolchain is located under:
~/workdir/bytedevkit-am62x/4.0/build/tmp/deploy/sdk
How to modify your toolchain
Currently the bytesatwork toolchain is generated out of the bytesatwork-minimal-image recipe. If you want to add additional libraries and development headers to customize the toolchain, you need to modify the bytesatwork-minimal-image recipe. It can be found under ~/workdir/bytedevkit-am62x/4.0/sources/meta-bytesatwork/recipes-core/images
For example if you want to develop your own ftp client and you need libftp and the corresponding header files, edit the recipe bytesatwork-minimal-image.bb and add ftplib to the IMAGE_INSTALL variable.
This will provide the ftplib libraries and development headers in the toolchain. After adding additional software components, the toolchain needs to be rebuilt by:
$ cd ~/workdir/bytedevkit-am62x/4.0
$ MACHINE=bytedevkit-am62x DISTRO=poky-bytesatwork EULA=1 . setup-environment build
$ bitbake bytesatwork-minimal-image -c populate_sdk
The newly generated toolchain will be available under:
~/workdir/bytedevkit-am62x/4.0/build/tmp/deploy/sdk
For additional information, please visit: https://docs.yoctoproject.org/4.0.9/overview-manual/concepts.html#cross-development-toolchain-generation.
Kernel
Download the Linux Kernel
Device |
Branch |
git URL |
|---|---|---|
bytedevkit-am62x |
baw-ti-linux-6.1.y |
Build the Linux Kernel
For both targets, an ARM toolchain is necessary. You can use the provided toolchain from Toolchain or any compatible toolchain (e.g. from your distribution)
Important
- The following tools need to be installed on your development system:
gitmakebc
Note
The following instructions assume, you installed the provided toolchain for the respective target.
Important
- The following tools need to be installed on your development system:
OpenSSL headers (Debian package:
libssl-dev)depmod(Debian package:kmod)
Download kernel sources
Download the appropriate kernel from Download the Linux Kernel.
Source toolchain
source /opt/poky-bytesatwork/4.0.9/environment-setup-aarch64-poky-linux
Create defconfig
make bytedevkit_am62x_defconfig
Build Linux kernel
make -j `nproc` Image dtbs modules
Install kernel and device tree
To use the newly created kernel, device tree and/or module, the necessary files need to be installed on the target. This can be done either via Ethernet (e.g.
scp) or by copying the files to the SD card.Note
For scp installation: Don’t forget to mount /boot on the target.
File
Target path
Target partition
arch/arm64/boot/Image/boot/Image/dev/mmcblk1p2arch/arm64/boot/dts/ti/k3-am625-bytedevkit.dtb/boot/k3-am62x-bytedevkit.dtb/dev/mmcblk1p2Note
After installing a new kernel, it often fails to load modules, as the _signature_ of the kernel changed and it fails to find its corresponding modules folder. This issue can often be resolved with a symlink:
ln -s /lib/modules/<EXISTING FOLDER> /lib/modules/`uname -r`
Otherwise, please follow the instructions to copy the kernel modules
Install kernel modules
To copy all available modules to the target, it’s best to deploy them locally first and then copy all modules to the target.
mkdir /tmp/bytedevkit-am62x make INSTALL_MOD_PATH=/tmp/bytedevkit-am62x modules_install
Now you can copy the content of the folder
/tmp/bytedevkit-am62xinto the target’s root folder (/) which is partition/dev/mmcblk1p2.
U-Boot
Download U-Boot Source Code
Device
Branch
git URL
bytedevkit-am62x
baw-ti-u-boot-2023.04
Build U-Boot
Install and get Dependencies
Hint
Probably some tools are missing on your host:
A list can be found here https://docs.u-boot.org/en/latest/build/gcc.html#building-with-gcc
A non-exhaustive list of (additional) necessary tools
sudo apt install bison flex swig libssl-dev python3-setuptools \ python-dev python3-dev python3-yaml python3-jsonschema
Build TF-A
Build OP-TEE
Build u-boot
You should have downloaded TI-linux-firmware and built TF-A, OP-TEE OS already.
Important
Use
am62x_bytedevkit_r5_defconfigandam62x_bytedevkit_a53_defconfiginstead of the TI defconfigs.Note
Clean command:
make ARCH=arm CROSS_COMPILE=aarch64-linux-gnu- O=<your_dir> distclean
Install SPL and U-Boot
SD Card
To use the newly created U-Boot, the necessary files need to be installed on the SD card. This can be done either on the host or on the target.
File
Target partition
Target partition label
File system
tiboot3.bintispl.binu-boot.img
/dev/mmcblk1p1(or/dev/sdX)
bootFAT32
You need to copy the files to the boot partition. The example assumes that the boot partition is mounted on
/media/${USER}/boot:cp tiboot3.bin tispl.bin u-boot.img /media/${USER}/boot/The next time the target is reset, it will start with the new U-Boot.
Hint
Copy the related files to SD card, see end of section TI u-boot build instructions
eMMC via SD Card
Copy the
tiboot3.bin,tispl.binandu-boot.imgto the SD Card rootfs partition.Program the
tiboot3.bin,tispl.binandu-boot.imgfrom the SD card to the eMMC.In the u-boot shell
run update_emmcOr manually by following commands
mmc dev 0 1 load mmc 1:2 ${loadaddr} tiboot3.bin mmc write ${loadaddr} 0x0 0x400 load mmc 1:2 ${loadaddr} tispl.bin mmc write ${loadaddr} 0x400 0xC00 load mmc 1:2 ${loadaddr} u-boot.img mmc write ${loadaddr} 0x1000 0x1000 mmc dev 0 0Note
The bootloader needs to be stored in the boot0 hardware partition of the eMMC. The layout of boot0 is defined so that it fits within 4 MiB, defined in blocks of 512 Bytes:
File
start
end
size
tiboot3.bin0x0000
0x0400
0x0400 512 KiB
tispl.bin0x0400
0x1000
0x0C00 1536 KiB
u-boot.img0x1000
0x2000
0x1000 2048 KiB